
an article written by Nitin Purwar, senior functional architect at UiPath.
Over the last ten years, I’ve had dozens of conversations with banking colleagues about regulatory compliance. As regulatory complexity increases, banks are still scrambling to figure out how to get compliance under control. According to Forbes, banking regulatory costs will rise from 4% to 10% of banking revenue by 2021.
Hiring more people to reduce regulatory burden isn’t a solution to the problem. Although automation holds much promise, some in banking have waning enthusiasm for Robotic Process Automation initiatives (see my colleague’s recent blog on this topic). In some cases this is due to banking RPA applications which have limited benefits, i.e., simple process automation with breaks and hand-offs to humans.
What’s needed to crack compliance management efficiency are automation of more complex banking workflows. To solve this challenge long-term, banking compliance leaders must carefully evaluate multiple technology investment considerations including:
. Solution coverage: End-to-end compliance coverage which integrates with all systems
. Agility: Flexibility to adopt the revisions in compliance requirements with minimal expense
. Cost-effectiveness: Cost elements may include a one-time license cost, ongoing maintenance, or a cost for reimplementation due to regulation changes
. Implementation timelines: Ease and speed of implementations to meet deadlines
. Enterprise-wide applicability: Capabilities to scale across enterprise geographies and cater to local dependencies
I am an RPA and machine learning (ML) technology enthusiast. I have experience in retail banking, wholesale banking, and banking operations. And I couldn’t be more enthused to share some of the new compliance use cases that the UiPath Enterprise RPA Platform supports with my peers and customers.
UiPath robots have learned to take on complex banking use case challenges. UiPath robots can run in attended, unattended, and hybrid modes and can be orchestrated centrally. Additionally, UiPath robots can work in tandem with humans or do a smooth hand-off which may be required for automating complex processes with human intervention. Human intervention scenarios include decisioning events related to dispute management, exceptions handling, alerts management, and credit approvals.
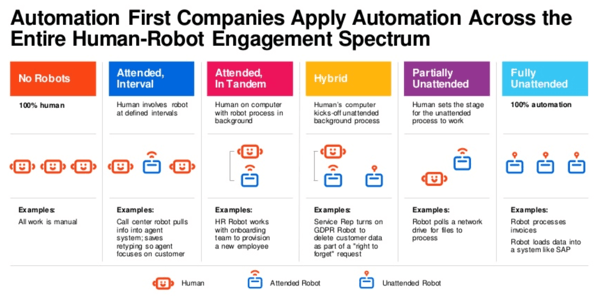
Source: Welcome to the Automation First Era: Your Guide to a Thriving Enterprise
Lending in general—and mortgage lending in particular—make up a big chunk of revenue for retail lenders. Both banks and regulators want to ensure responsibly managed customer experiences in these remediation scenarios:
. Applying incorrect interest rates
. Overcharging fees/late payment deductions
. Erroneous equated monthly installment (EMI) deductions
. Customer complaint handling
In most cases, remediations are manually managed or done as a result of customer complaints, audit findings, or due to a regulatory push. Due to large volumes, completing all the remediation steps starting with scoping a customer refund or adjustment can take months before the error can be resolved.
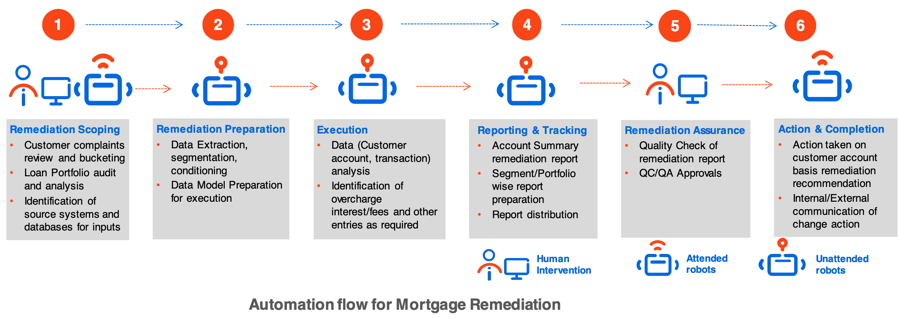
RPA can be used to automate these processes. The illustration below shows the typical workflow for a mortgage remediation effort. The symbols represent the type of automation (attended/unattended) used for automating the overall process. Human intervention steps are built into the automation flow. The tips below summarize how the activities are automated with the UiPath Platform:
1. Data extraction and preparation: An important step to begin the mortgage remediation journey is to prepare the necessary data. RPA robots help in extracting data from required source systems and databases and put the data into the required format.
2. Execution: Includes automating the verification of account entries and identifying incorrect fees or interest rate calculations where applicable. Based on a set of rules, UiPath robots identify any missing details in the accounts if there are any gaps.
3. Action: UiPath robots can complete the remediation of an account by completing the general ledger (GL) entries for respective customers where discrepancies are identified. Also, in cases where information is required from customers, emails or notifications are sent. The process completes with refunds or payments to customer accounts which can be completed by a UiPath robot or sent for approval by a human first.
4. Remediation reporting: Most of these activities are associated with reporting and reconciliation; robots create an audit log of the activities performed and publish it for review.
Customer due diligence (CDD) and know your customer (KYC) are critical customer onboarding functions which are highly regulated. These due diligence processes help banks to assess the risk of new customers, and to determine the products and relationship that the bank can develop with them.
Banks are increasingly looking to automate these CDD and KYC processes to get better control of compliance costs:
. Reducing the time to onboard a customer (which sometimes stretches from days into weeks)
. Improving the customer experience by digitizing the onboarding process
. Shifting from largely manual processes to automated processes
. Improving the quality of due diligence
While most banks have experimented with KYC automation, end-to-end KYC automation is uncommon because of the volume of unstructured data and channels that are involved.
To automate this process, both attended and unattended robots which can hand-off to a human are required. In order to ensure an omni-channel automation experience, technologies that support conversational understanding artificial intelligence (AI) are also required.
The figure below shows the automated steps in the KYC/CDD journey. Note the smooth transitioning between robots. In case of onboarding corporate customers, our robots can add even more value as the number of verifications needed is much higher, involving higher human effort and lengthening the process to even one month, having a huge impact on the customer experience.
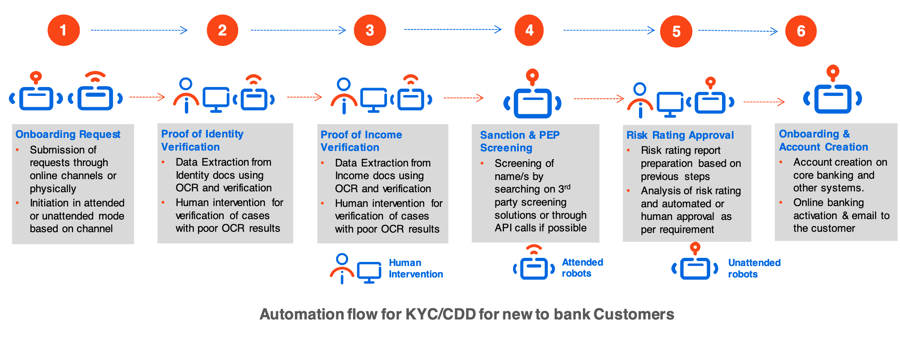
Let me summarize the automation using the UiPath Enterprise RPA Platform:
Onboarding request: Banks providing an omnichannel experience ensure that customers can submit requests online through chat interfaces or at a kiosk or bank branch. Integration of the UiPath Platform with online/chat interfaces ensure that UiPath robots can take the request, flag things if necessary, and identify missing information.
Identity/income verification: These are the most important steps to perform KYC and require validation of verification documents. This can be automated by extracting required information using UiPath optical character recognition (OCR) from the KYC documents and verifying against government or public databases. Depending on the quality of documents this step can be performed in an attended mode or with a human validation step for rectifying incorrectly extracted information.
Sanction and Politically Exposed Person (PEP) screening: Depending on the process used by a bank, this automation can be performed in an unattended mode by checking the names against sanctions and PEP solutions provided by third-party providers.
Risk rating approval: Based on the completion of the above steps, the UiPath robot can create a risk profile of the customer which can then be sent for a final approval (or auto approved if required) based on the risk category.
Onboarding and account creation: Post profile approval, UiPath robots can create an account of the customers in the required core banking and other support systems. The UiPath robots can also activate online banking and a debit or credit card.
The UiPath Enterprise RPA Platform helps banking institutions achieve automation at scale allowing banks to successfully reduce regulatory compliance burdens, deliver omni-channel customer experiences, and control costs.
The UiPath Platform has pre-built advanced features which provide complete and expansive coverage of banking RPA use cases. As an example, because regulatory compliance functions provide a true line of defense for banks, there are many processes where human validation or decision making is necessary. The UiPath RPA Platform can cater to these scenarios.
UiPath robots also leverage rapid design and build capabilities augmented by thousands of activities. These activities can be dragged and dropped to build automation workflows. The latter are are easy to implement and easy to modify. Banks can ensure compliance across all operating geos by automating processes via central management using UiPath Orchestrator.
These enterprise RPA-scaling capabilities enable banks to achieve compliance, avoid deadline-related fines, derive more value from their RPA initiatives, and better protect their business.
To learn more about banking compliance use cases and what UiPath for banking and capital markets has to offer, check out banking RPA components and accelerators on the UiPath Go! Marketplace.
About the author
Strategy and Transformation professional with a rich experience of managing strategic projects/programmes in different work streams in BFSI viz., Wholesale Banking, Regulatory, Compliance, Technology, Operations, Offshoring, Process Modelling, HR.
Have received recognition for stakeholder management, leadership, innovation and application of six sigma methodologies in project management.
Graduate from IIT BHU, Varanasi and Post Graduate from IMT Ghaziabad with entrepreneurial inclination.
Learn more:
Banking 4.0 – „how was the experience for you”
„To be honest I think that Sinaia, your conference, is much better then Davos.”
Many more interesting quotes in the video below: