BIS and central banks test post-quantum cryptography in payments

Protecting financial systems from the potential threat posed by quantum computers requires a proactive and coordinated approach. Challenges go beyond technical aspects and include awareness, resource allocation, competence development, inventory, pilots, governance and more.
Project Leap Phase 2, a collaboration between the BIS Innovation Hub Eurosystem Centre, the Bank of Italy, the Bank of France, Deutsche Bundesbank, Nexi-Colt, and Swift, tested post-quantum cryptography in an operational payment system.
The experiment replaced traditional digital signatures with post-quantum cryptography, while sending liquidity transfers. It involved modifying numerous system components to ensure compatibility with updated cryptographic libraries.
Quantum computers present a cyber threat to financial data
Quantum computers, should they reach sufficient size and power, may be able to break the encryption schemes widely used today to secure financial transactions, communication and data. This makes quantum computing one of the most significant cybersecurity threats facing the financial system, potentially exposing financial transactions to attack.
While it is still unclear when quantum computing technology might be adopted on a large scale, its potential as a cyber threat to the financial system is already a matter of concern. Malicious actors can intercept and store confidential, classically encrypted data with the intention of decrypting it later when quantum computers become powerful enough to do so. This means that data stored or transmitted today are, in fact, exposed to „harvest now, decrypt later” attacks by a future quantum computer.
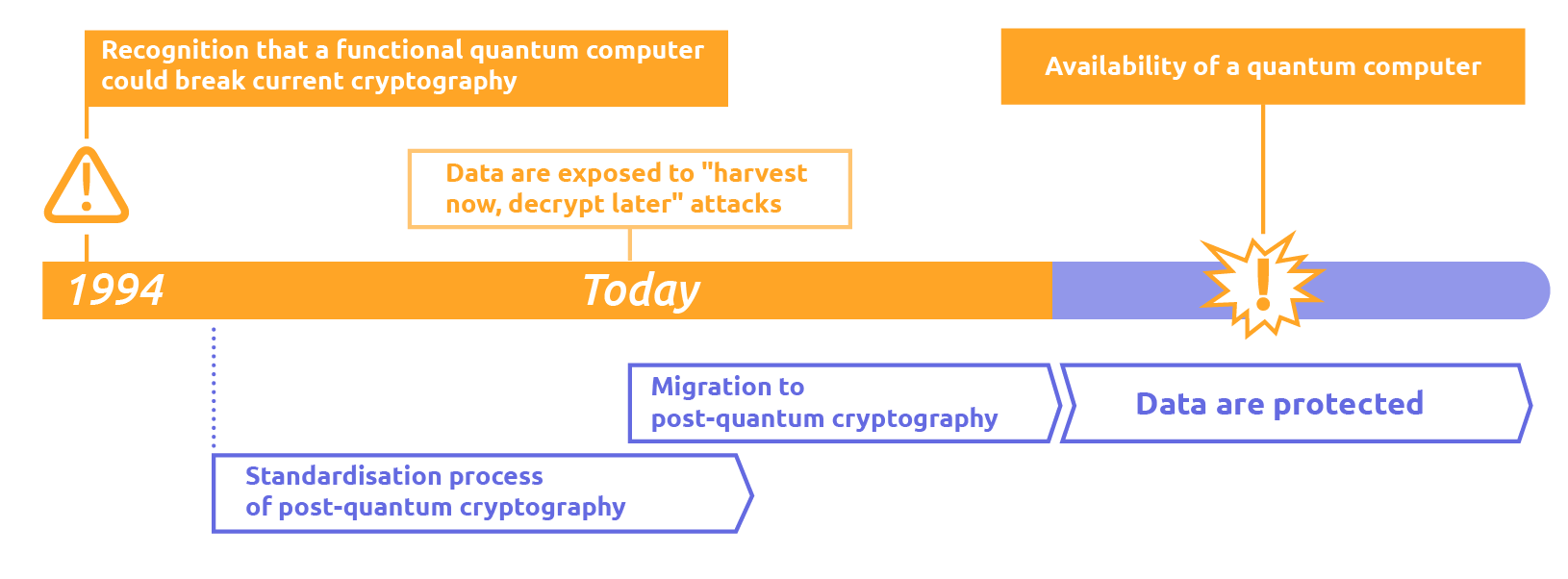
To address these risks, the financial sector needs to pre-emptively implement robust communication and data protection technologies. Given the long-term sensitivity of financial data and the complexity of IT systems, a transition phase should be initiated well in advance so that quantum-resistant encryption schemes can be implemented.
Preparing for the cyber threat of quantum computers
The BIS Innovation Hub and its partners have successfully completed two phases of Project Leap.
Leap Phase 1, a collaboration between the BIS Innovation Hub, Bank of France, and Deutsche Bundesbank, tested the implementation of post-quantum cryptography between two central bank IT systems. A traditional public key algorithm was implemented alongside quantum-resistant algorithms in a hybrid encryption scheme, achieving quantum-resistant confidentiality of payment messages sent across two distanced IT systems. The project demonstrated that implementing quantum-safe cryptography in the financial system is feasible and identified performance impacts and the need for more testing.
Leap Phase 2, a collaboration between the BIS Innovation Hub, Bank of Italy, Bank of France, Deutsche Bundesbank, Nexi-Colt and Swift, tested post-quantum cryptography in an operational payment system. Most payment systems rely on public key cryptography and require long-term data confidentiality, making them vulnerable to the quantum threat. At the same time, as the backbone of modern economies, payment systems are critical to the smooth functioning of commerce, finance, and daily life – protecting them is essential to preserving financial stability.
By replacing traditional digital signatures with post-quantum cryptography while sending liquidity transfers, Leap Phase 2 demonstrated the feasibility of quantum-proofing payment systems.
The two successful technical experiments of Project Leap 1 and 2 – together with accompanying studies on the risks and opportunities from quantum computing and roadmap to quantum-readiness – have laid important groundwork for the quantum-safe journey of the financial system. This collaborative initiative underscores the commitment of central banks to proactively safeguarding the integrity and resilience of financial infrastructures. They reflect a forward-looking dedication in ensuring that payment systems remain secure in the face of emerging technological threats.
Read more details below:
Project Leap Phase 2 confirmed that post-quantum cryptography can be successfully implemented in payment systems.
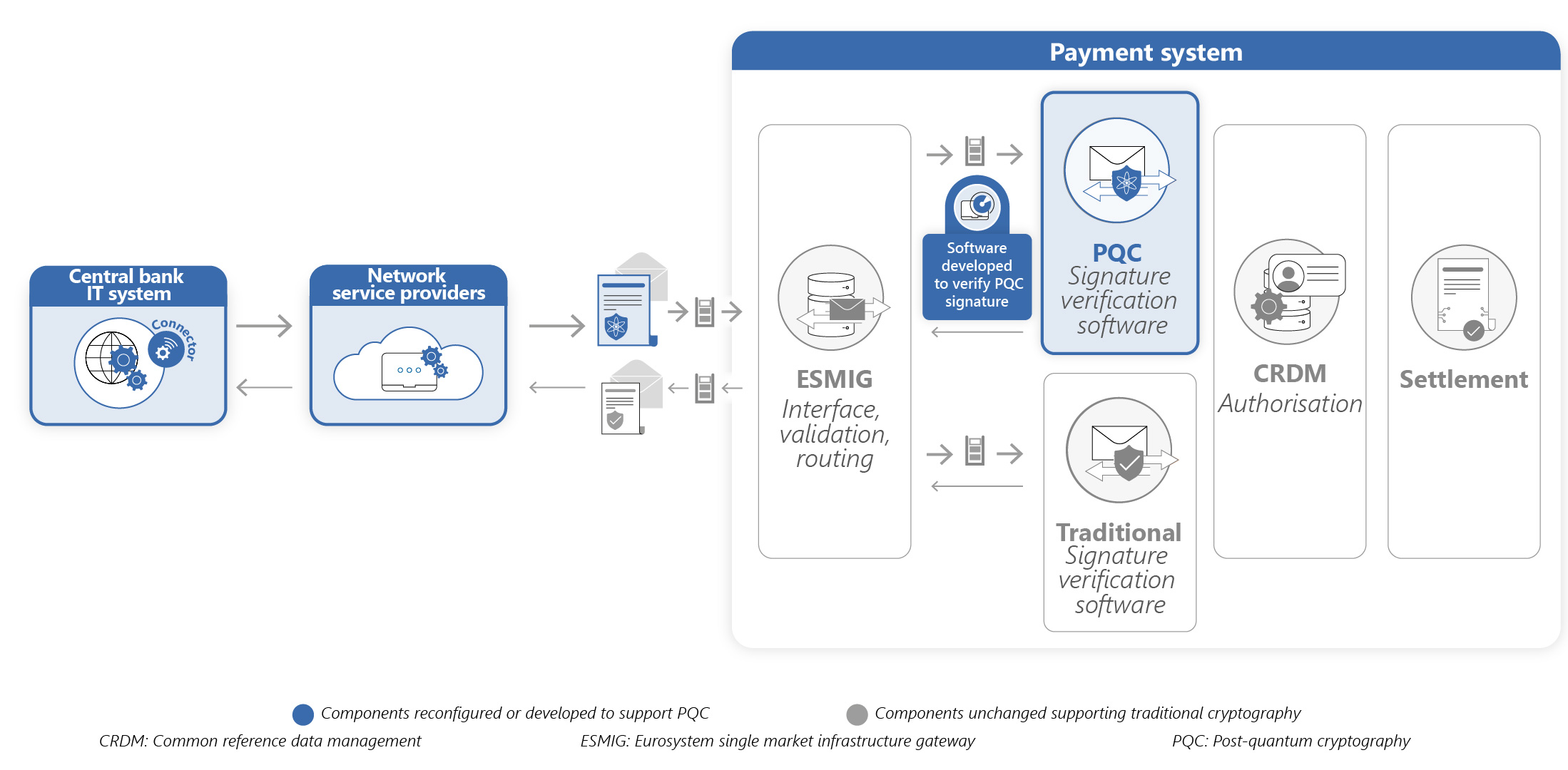
The experiment replaced traditional digital signatures with post-quantum cryptography in an existing payment system, while sending liquidity transfers. It involved modifying numerous system components to ensure compatibility with updated cryptographic libraries. All test scenarios were successfully executed, demonstrating the feasibility of migrating payment systems to post-quantum cryptography. Besides demonstrating functional correctness, the experiments highlighted that post-quantum cryptography leads to significantly higher processing time than traditional algorithms, which will need to be taken into consideration when planning migration.
_____________
Report: Project Leap Phase 2: Quantum-proofing payment systems
The project report outlines key functional and technical findings related to post-quantum cryptography digital signature implementation in a payment system. It also describes learnings related to performance, interoperability, and cryptographic agility. The conclusions underscore the need for timely preparation to ensure the financial system is resilient against emerging threats.
Dariusz Mazurkiewicz – CEO at BLIK Polish Payment Standard
Banking 4.0 – „how was the experience for you”
„To be honest I think that Sinaia, your conference, is much better then Davos.”
Many more interesting quotes in the video below: