
Enhancing cross-border payments has been a G20 priority since 2020. This ambitious programme requires action by individual jurisdictions and payment systems. The Bank for International Settlements’ Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures (CPMI) survey results show determined progress: the vast majority of payment systems have or are in the process of implementing at least one action that the G20 considers to be relevant to enhance cross-border payments.
Despite the promising number of initiatives planned to enhance cross-border payments, the survey results also highlight potential areas for further work. Projects to enhance cross-border payments cannot be seen in isolation and should complement domestic projects, given that the first and last miles of cross-border payments are typically processed in a domestic payment system.
Central banks, in their roles as catalyst and operators, are key to bringing cross-border payments forward. International organisations and standard-setting bodies, such as the CPMI, the IMF and the World Bank, can support central banks in their ambitions.
###
The CPMI launched in 2023 a monitoring survey among central banks on the updated roadmap’s three priority themes: (i) payment system interoperability and extension; (ii) data exchange and message standards; and (iii) legal, regulatory and supervisory frameworks.
This report presents the survey findings for each of the priority themes. Respondents provided information on operational or planned real-time gross settlement (RTGS) systems, fast payment systems (FPS) and deferred net settlement (DNS) systems within their jurisdiction. These include payment systems owned and operated by the public sector as well as the major private systems.
This report is based on responses from 71 central banks, with broad coverage of both advanced economies (AEs) and emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs). It covers 166 operational payment systems, including 69 RTGS systems, 45 FPS and 52 DNS systems, in addition to two planned RTGS systems and eight planned FPS.
(ii) Data exchange and message standards
Data standards, formats and frameworks vary significantly across jurisdictions, infrastructures and message networks. As a result, the data carried in most cross-border payment messages are often not harmonised, reducing straight-through processing and automated reconciliation. The G20 cross-border payments programme identified the fragmentation of payment messaging standards as one of the factors contributing to the frictions in cross-border payments.
Promising adoption of ISO 20022 sets the scene for its harmonised use for crossborder payments
The growing global adoption of the international financial messaging standard ISO 20022 by payment systems and financial institutions offers the prospect of greater interoperability, with benefits for cross-border payments.
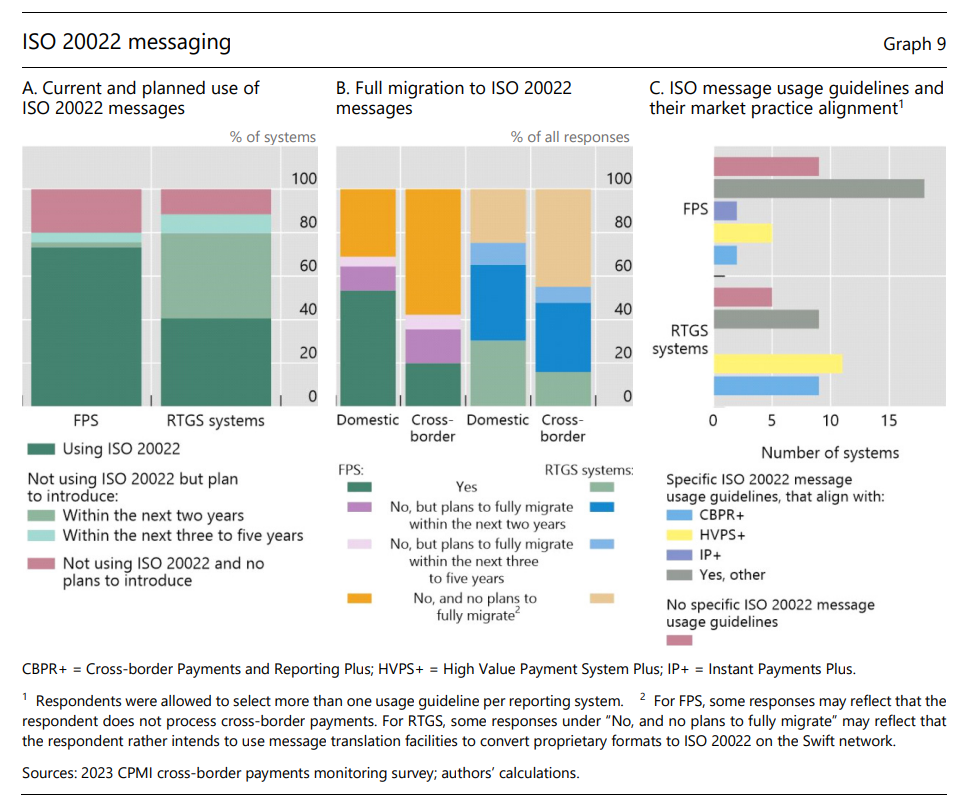
Many payment systems, particularly FPS, have already implemented ISO 20022 (73% of the 45 reported FPS and 41% of the 69 reported RTGS systems) (Graph 9.A). Payment systems in Europe and Asia-Pacific have implemented ISO 20022 messaging ahead of systems in the Americas, Middle East and Africa.
After including planned implementations of ISO 20022 messaging, 80% of FPS and 88% of RTGS systems are expected to be processing ISO 20022 messages within the next five years. Within the same period, 69% of FPS and 75% of RTGS systems plan to fully migrate to ISO 20022 messages for domestic payments, while only 42% of FPS and 55% of RTGS systems plan to fully migrate to it for cross-border payments (Graph 9.B). Full migration to ISO 20022 messages6 for cross-border payments might first be achieved in Europe, with 81% of FPS and 58% of RTGS systems having plans to fully migrate within five years.
Inconsistencies in the implementation and use of ISO 20022 for cross-border payments risks undercutting some of its benefits. Of those already processing ISO 20022 messages, 27% of FPS and 18% of RTGS systems have not implemented ISO 20022 message usage guidelines, and among those that have, there is significant variance as to which market practice they align with (Graph 9.C). Given the rapid adoption of ISO 20022 messaging under way, the coming years will be crucial for harmonising its use to fully leverage its potential for cross-border payments. In October 2023 (after this survey was undertaken), the CPMI published ISO 20022 harmonised data requirements with the aim of addressing this fragmentation issue.
Application programming interfaces have potential and room for harmonisation
Application programming interfaces (APIs) can facilitate more efficient and faster cross-border payments by reducing manual intervention and facilitating more timely data exchange across the payment chain.
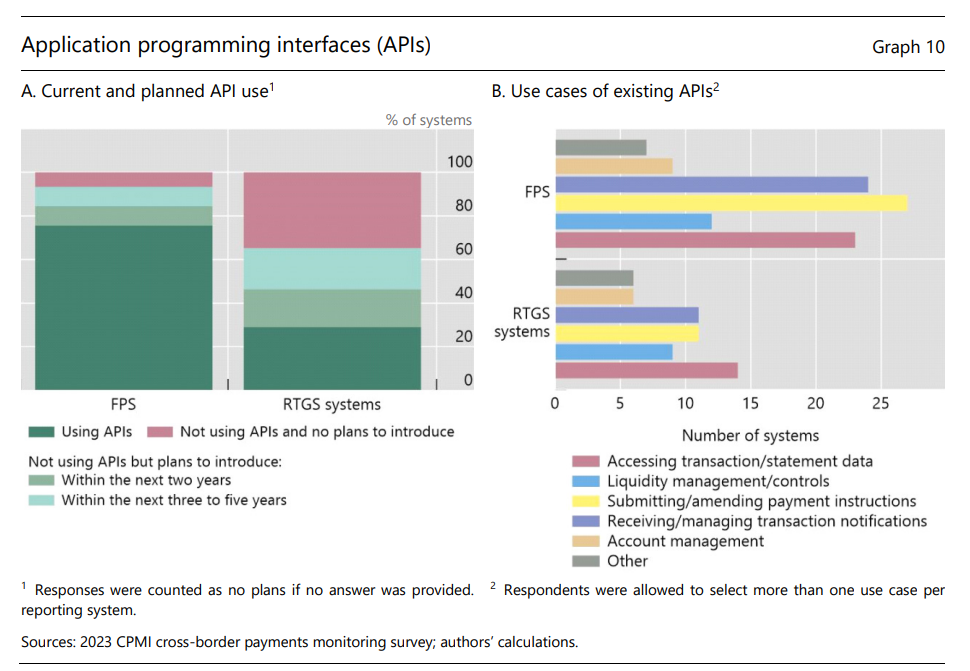
APIs are increasingly being adopted by payment systems and PSPs, with 65% (or 45) of RTGS systems and 93% (or 42) of FPS planning to use APIs within the next five years (Graph 10.A). This is especially so for central banks from the Middle East and Africa. Existing use cases include submitting or amending payment instructions and for information exchange, such as transaction data access and transaction notifications (Graph 10.B).
API protocols are arguably less harmonised than ISO 20022 data models, impeding interoperability and reducing the potential benefits of their implementation. Supporting greater harmonisation of APIs has thus been identified by the G20 cross-border payments programme as a priority for achieving cheaper, faster, more transparent and accessible cross-border payments. Of the payment systems currently using APIs, around half indicated that the APIs are based on international or national standards.
Dowload the full report here
CPMI Brief No 5 – Steady as we go: results of the 2023 CPMI cross-border payments monitoring survey
Banking 4.0 – „how was the experience for you”
„To be honest I think that Sinaia, your conference, is much better then Davos.”
Many more interesting quotes in the video below: